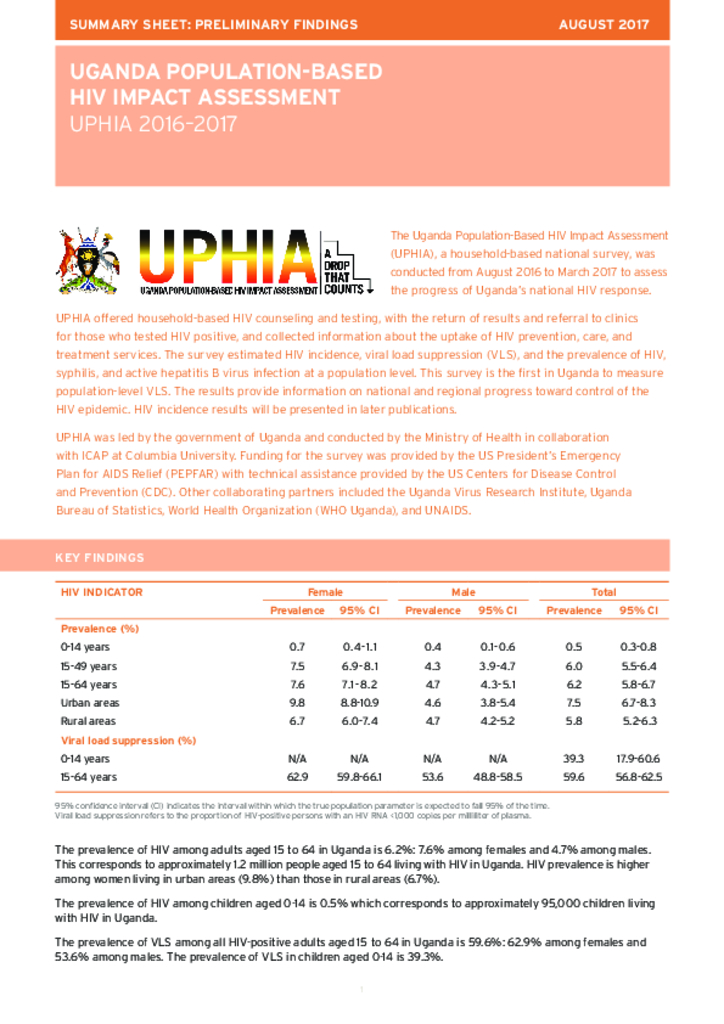
The Uganda Population-Based HIV Impact Assessment (UPHIA), a household-based national survey, was conducted from August 2016 to March 2017 to assess the progress of Uganda’s national HIV response. UPHIA offered household-based HIV counseling and testing, with the return of results and referral to clinics for those who tested HIV positive, and collected information about the uptake of HIV prevention, care, and treatment services. The survey estimated HIV incidence, viral load suppression (VLS), and the prevalence of HIV, syphilis, and active hepatitis B virus infection at a population level.
This survey is the first in Uganda to measure
population-level VLS. The results provide information on national and regional progress toward control of the HIV epidemic. HIV incidence results will be presented in later publications.
Uganda was ranked 18th out of the 22 tuberculosis (TB) high-burden countries in the world during 2009. The Annual Risk of TB Infection (ARI) for Uganda is estimated at 3 percent. The incidence of TB is 330/100,000 population for all TB cases and 136/100,000 population for sputum smear-positive pulmonary TB. The death rate among sputum smear-positive pulmonary TB patients registered during 2008 was 5.3 percent in 2008
Uganda faces a high burden of tuberculosis (TB), but accurate estimates of the burden of TB in the country were unavailable. A national prevalence survey was therefore conducted from October 2014 to July 2015 to achieve the primary objective of estimating the prevalence of bacteriologically confirmed pulmonary TB (PTB) in the population aged >15 years in Uganda. In addition, the survey sought to estimate—
The National malaria Control policy provides a framework and environment within the overall context of the national health policy and the health sector strategic and investment plan of the country for sustainable malaria prevention and control.
This is the 12th issue of the Uganda Malaria Quarterly Bulletin that focuses on the fourth quarter of 2015. The aim of this bulletin is to inform district, na-tional, and global stakeholders on progress achieved and challenges encountered in malaria control in Uganda. Most importantly, it is to encourage use of this information at all levels in order to foster improvement of our efforts and to highlight achievements and create awareness for increased resource mobilization& alloca-tion in order to maintain the gains we have achieved
The 2014-15 Uganda Malaria Indicator Survey (2014-15 UMIS) was implemented by the Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS) and the National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP) of the Uganda Ministry of Health from December 2014 to January 2015. The funding for the UMIS was provided by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and the United Kingdom Department for International Development (DFID). ICF International provided technical assistance as well as funding to the project through The DHS Program, a USAIDfunded project providing support and technical assistance in the implementation of population and health surveys in countries worldwide
The Prevention 2020 Road Map provides the basis for a country-led movement to scale up HIV prevention programmes as part of Fast-Tracking a comprehensive response to meet global and national targets and commitments to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
Uganda has made great strides in reducing overall HIV incidence, AIDS related mortality, new infections among infants, and HIV prevalence. While the current improvements have been made, the scope, coverage and intensity of interventions are still inadequate to move the country to epidemic control and sustain the trend in reducing new HIV infections.
Over the years, Uganda's efforts in combating HIV and AIDS have registered considerable progress. We succeeded in bringing down the HIV prevalence rate from a peak of 18 per cent in the 90s to 6-7 percent at the turn of the century. In the last 3-4 years there have been significant improvement in the reduction of new HIV infections
The 2014-15 Uganda Malaria Indicator Survey (2014-15 UMIS) was implemented by the Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS) and the National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP) of the Uganda Ministry of Health from December 2014 to January 2015. The funding for the UMIS was provided by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and the United Kingdom Department for International Development (DFID). ICF International provided technical assistance as well as funding to the project through The DHS Program, a USAID-funded project providing support and technical assistance in the implementation of population and health
surveys in countries worldwide.
The Malaria Control Strategic Plan is an instrument of the Government’s commitment and determination to address the malaria problem in Uganda in a sustainable manner. The plan is a complement to the broader five-year Health Sector Strategic Plan which again is part of the Poverty Eradication Action Plan where malaria features as a high priority health and poverty issue.
This is the 14th issue of the Uganda Ma-laria Quarterly Bulletin that focuses on the second quarter of 2016. The aim of this bulletin is to inform district, national, and global stake-holders on progress achieved and challenges encountered in malaria control and reduction in Uganda. Most importantly, it is to encourage use of this information at all levels in order to foster improvement of our efforts and to high-light achievements and create awareness for increased resource mobilization& allocation in order to maintain the gains we have achieved