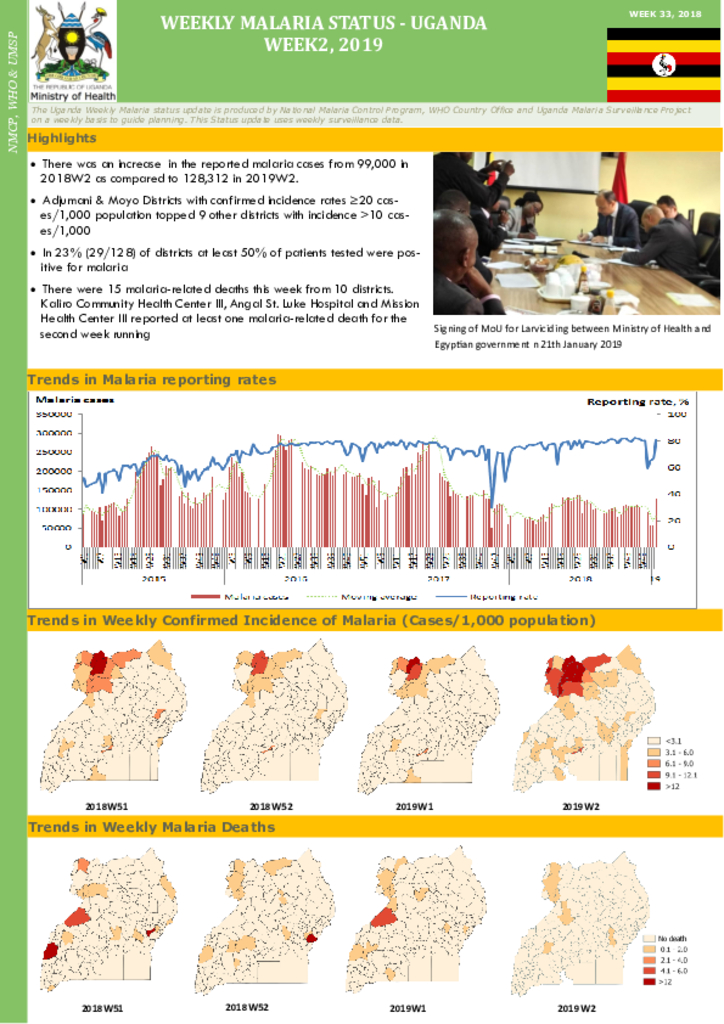
This publication is about the malaria case statistics of Uganda in the 2nd week of 2019.
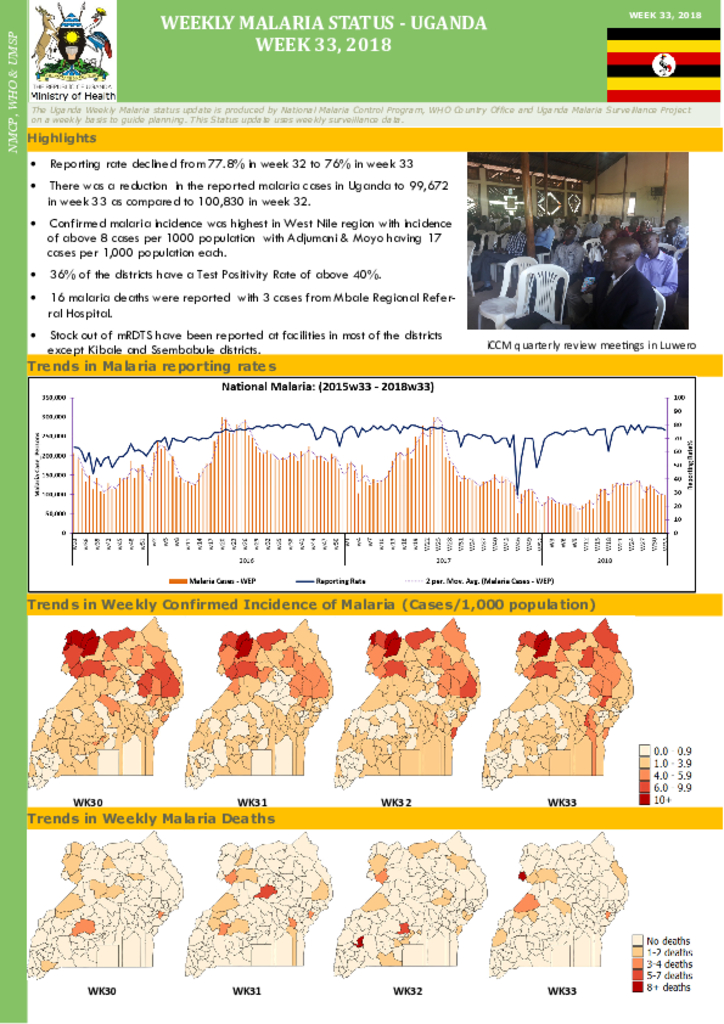
This publication is about the statistics of the malaria case weekly reporting in Uganda.
This Summary presents an overview of the results of thefirst, second and third rounds of WHO Product Testing of malaria antigen-detecting RDTs completed in 2008, 2009 and 2011 respectively, and is published in conjunction with the release of the results of Round 3. The results of the three rounds of testing should be considered as a single data set.
The aim of this bulletin is to inform district,national, and global stake-holders on progress achieved and challenges encountered in malaria control and reduction in Uganda. Most importantly, it is to encourage use of this information at all levels in order to foster improvement of our efforts and to high-light achievements and create awareness for increased resource mobilization& allocation in order to maintain the gains we have achieved.
This publication is about the malaria statistics of Uganda.
This document reflects the recommendations of the OSP report. The aim is to set out a revised and clearly defined strategic framework which takes into account AMREF’s comparative strengths, while also considering the goalsand objectives of the Roll Back Malaria Partnership Global Strategic Plan 2005-2015 and the specific goals and objectives of the RBM sub-regional networks.
This report presents the findings from the Uganda Malaria Indicator Survey (UMIS) directed by ICF Macro under a contract with the Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS), the Uganda Malaria Surveillance Project Molecular Laboratory at Mulago Hospital, and the National Malaria Control Programme of the Uganda Ministry of Health.
This issue also shows you how the National Malaria Control Program has also been energized with the hiring of new staff.
This interagency handbook was developed by the Roll Back Malaria(RBM) Technical Support Network on Complex Emergencies. It focuses on effective malaria control responses to complex emergencies, particularlyduring the acute phase when reliance on international humanitarian assistance is greatest. It provides policy-makers,planners, field programme managers and medical coordinators with practical guidance on designingand implementing measures to reduce malaria morbidity and mortality.
This publication is about how to make safe blood especially for tranfusion. Making blood free of contegious diseases like HIV/AIDS thus reducing the risk of transmitting such diseases.
The objective of this paper is to demonstrate how and why HIV should be considered in each of the PEAP pillars. It provides a set of core questions, which need to be considered in developing Sector PEAP Review Papers (SPRP) and the construction of each pillar as well as suggestions to help guide the PEAP revision teams at various levels.
This document presents a draft verbal autopsy instrument based on best judgement and previousexperience in a variety of settings including outbreaks and research. It has been circulated widely toprofessionals involved in previous outbreaks and revised accordingly.
This questionnaire is a first attempt at developing a standard questionnaire. It is part of a wider effort by the Global OutbreakAlert and Response Network (GOARN) to develop tools for testing in advance of outbreak
situations. The draft needs to be field tested, validated, and if necessary revised, before it can beconsidered as a standard questionnaire.